Brenda Kintaitė1, Paulina Tekoriutė1, Ieva Petrauskaitė1, Monika Matuliauskaitė1, Aistė Šakalytė1, Julius Vidikas2
1 Lithuanian University of Health Sciences, Academy of Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Kaunas, Lithuania
2 Lithuanian research center of health sciences
Abstract
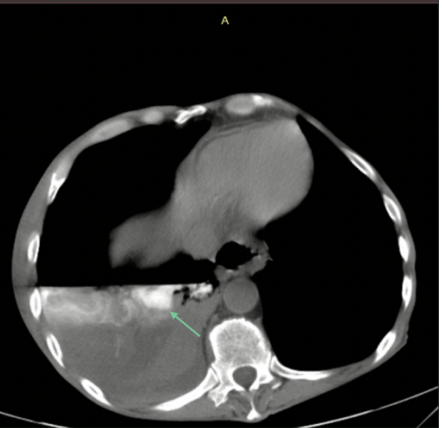
Background: esophagopleural fistula is a rare pathological connection among digestive and respiratory systems. The are many different causes of it but usually, it is related to endoscopic and surgical interventions, oncological processes. The symptoms of this disease are non-specific, patients complain of retrosternal chest pain, fever, dyspnoea, dysphasia, cough. The most valuable test for diagnosing esophagopleural fistula is chest computed tomography (CT) with intravenous contrast. Possible treatments are conservative or invasive
Aim: this study aimed to reveal the clinical manifestations and managements of esophagopleural – fistula, to review the latest scientific literature on this topic, and to acquaint doctors of various fields with the clinical features, diagnosis and treatment options of this rare pathology.
Methods: a review of the literature using the PubMed database, a selection of scientific publications addressing the topic of esophageal pleural fistula, and a clinical case of the disease was presented.
Conclusion: the esophagopleural junction is a rare complication with no specific clinical manifestations which complicates the diagnosis of pathology. A detailed history and prompt diagnosis are essential because esophagopleural fistula is associated with life-threatening complications and high mortality. Chest CT with intravenous contrast is the most accurate method for diagnosing this pathology. Although pleuroesophageal fistula can be treated conservatively in some cases, it is extremely rare for this treatment to be effective. Endoscopic treatment options and sometimes surgical interventions are much more common.
Keywords: esophagopleural fistula, pneumohidrothorax, esophageal stents, stents.