Andrius Račiūnas1
1Royal London Hospital, Barts Health NHS Trust, Ear, Nose & Throat department, London, United Kingdom
Abstract
Introduction. Laryngeal cysts are benign fluid-filled non-infected sacs that can appear in different anatomical parts of the larynx. They are most commonly found in the supraglottic area. Symptoms include voice changes, foreign body sensation, snoring, obstructive sleep apnea, sore throat, dysphagia/odynophagia, dyspnea, however, most of the cysts found are incidental. Flexible nasendoscope and CT/MRI is used to diagnose and microlaryngoscopy and a laser is the main method of removing laryngeal cysts.
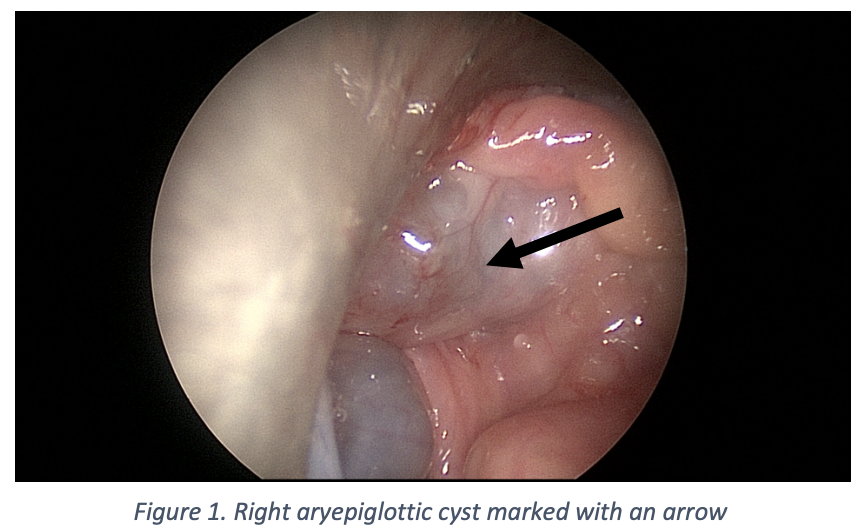
Clinical case. A 25-year-old gentleman presented to ENT Head & Neck clinic following a 2-month history of progressive difficulty in swallowing, hoarse voice, difficulty in breathing, and wheezing. A flexible nasendoscopy was performed which identified a large ball shape 4 cm supraglottic cyst in the right aryepiglottic fold which was valving and blocking the view of his vocal cords. A patient was taken to the theatre on the same day due to late presentation and fear that the cyst may rupture and cause airway problems. He had a microlaryngoscopy and laser excision of the right aryepiglottic fold cyst.
Conclusion. A patient who presented with longstanding and progressive airway symptoms should be urgently seen in the A&E. Late presentation increases the risk of sudden death due to airway deterioration. It is important to collect any comprehensive history before any anaesthesia. CT/MRI is recommended for preoperative planning. In some cases, time can be limited due to the risk of sudden airway deterioration.
Keywords. Laryngeal cyst, aryepiglottic cyst, airway emergency.